Glory Tips About Are Stacked Bar Charts Hard To Read How Make Curve Graph In Excel

For example, a stacked bar chart is great for comparing numeric values between levels of a categorical variable.
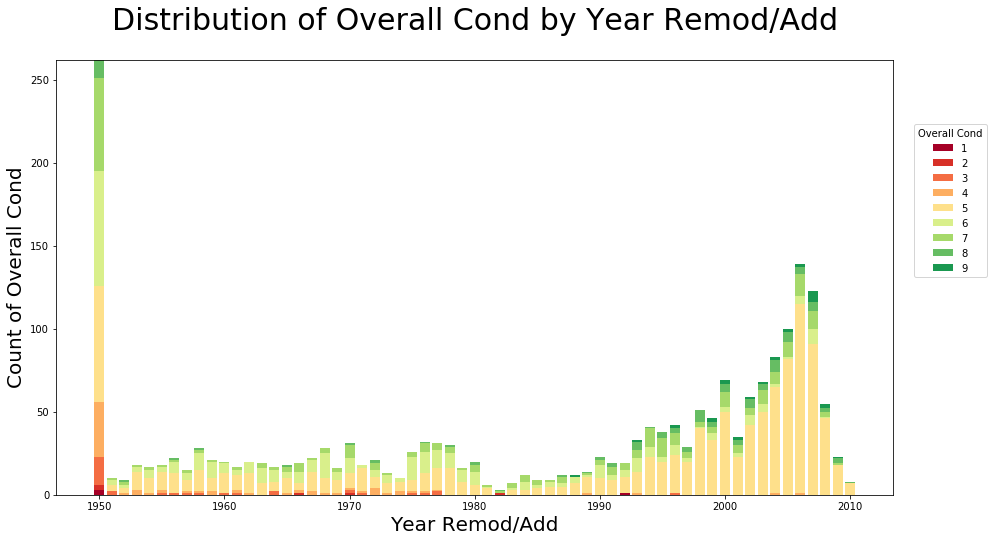
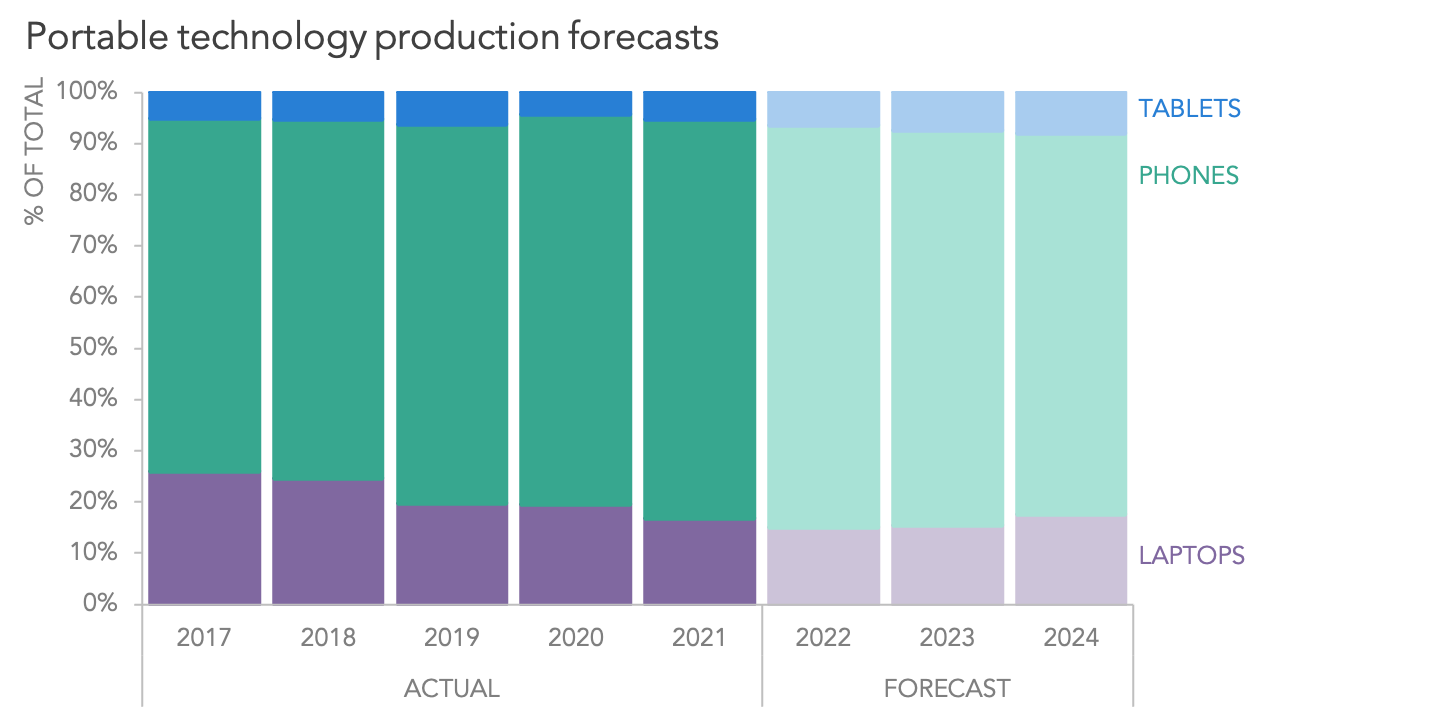
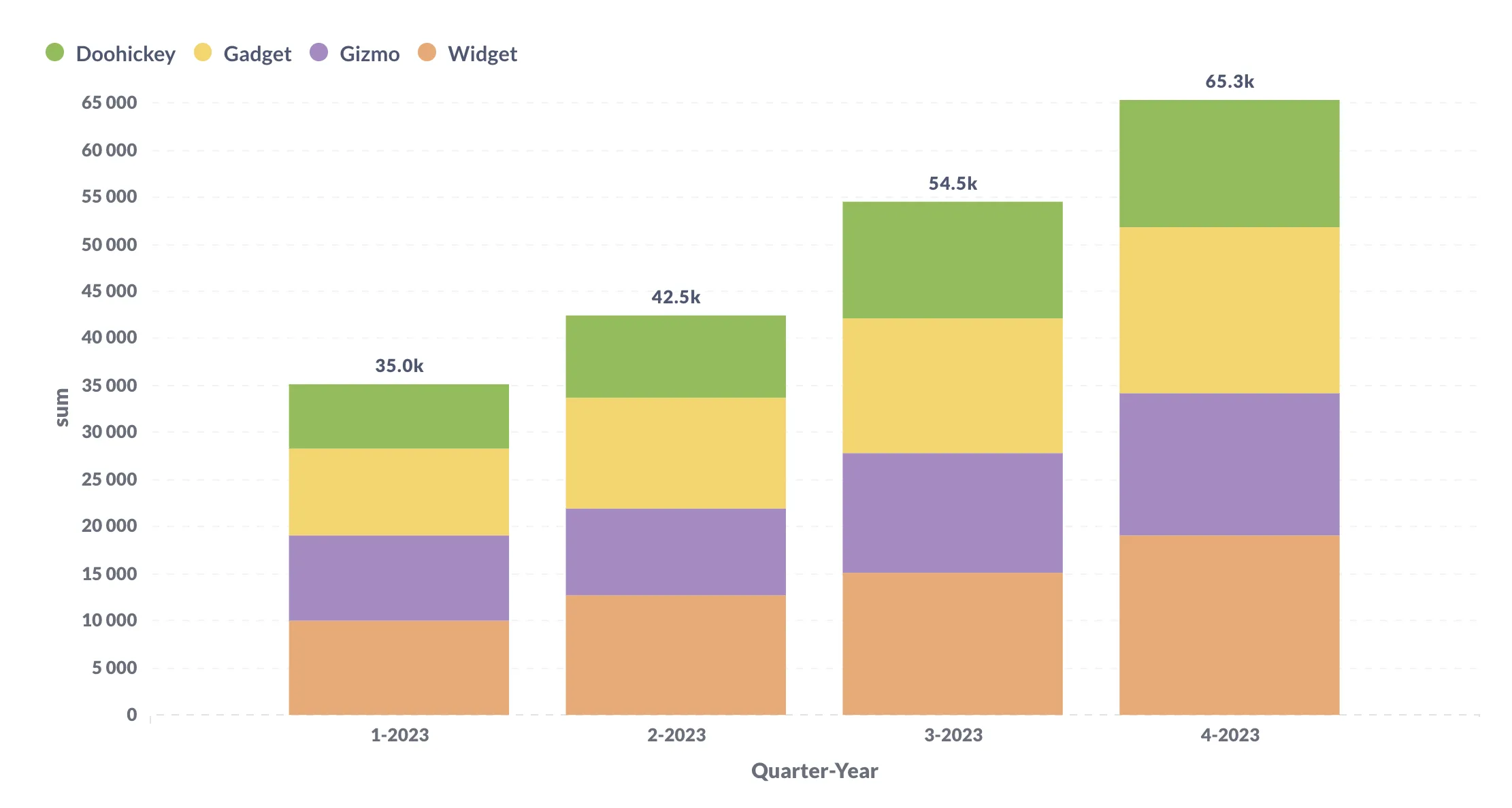
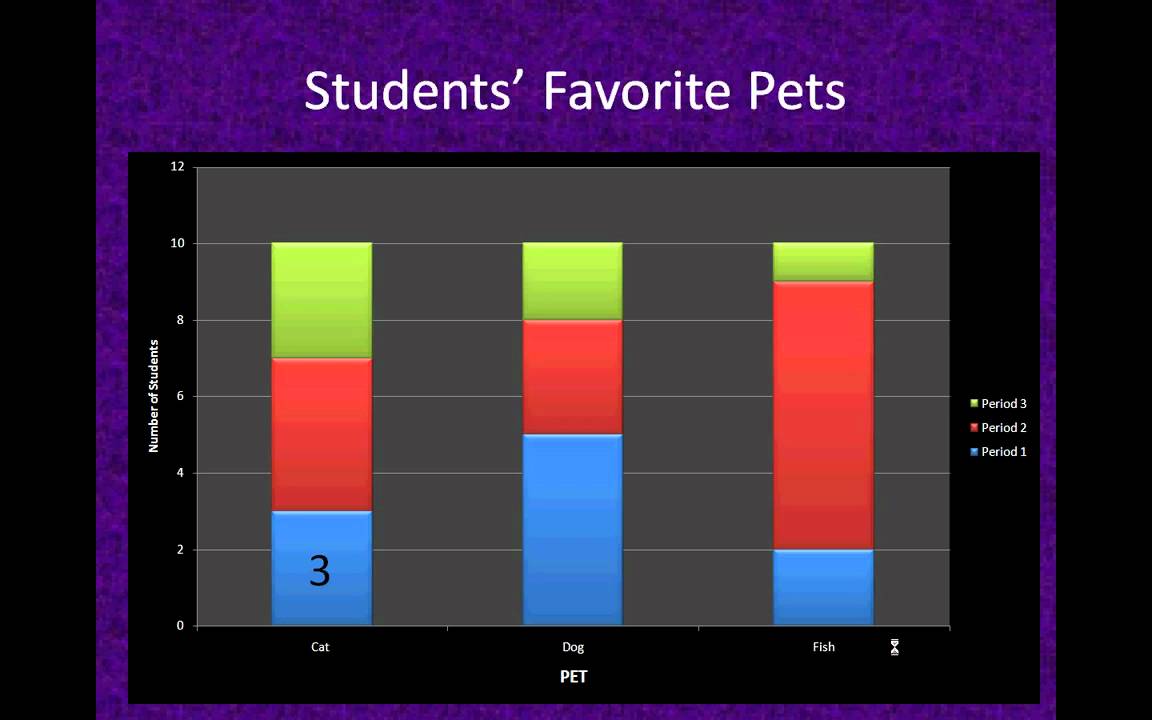
Are stacked bar charts hard to read. It’s used to visualize the total of grouped data points while also showing the comparative sizes of each data point’s component parts. This makes them a good choice for inventory, sales, and other countable data points. Also called a stacked bar or column chart, they look like a series of columns or bars that are stacked on top of each other.
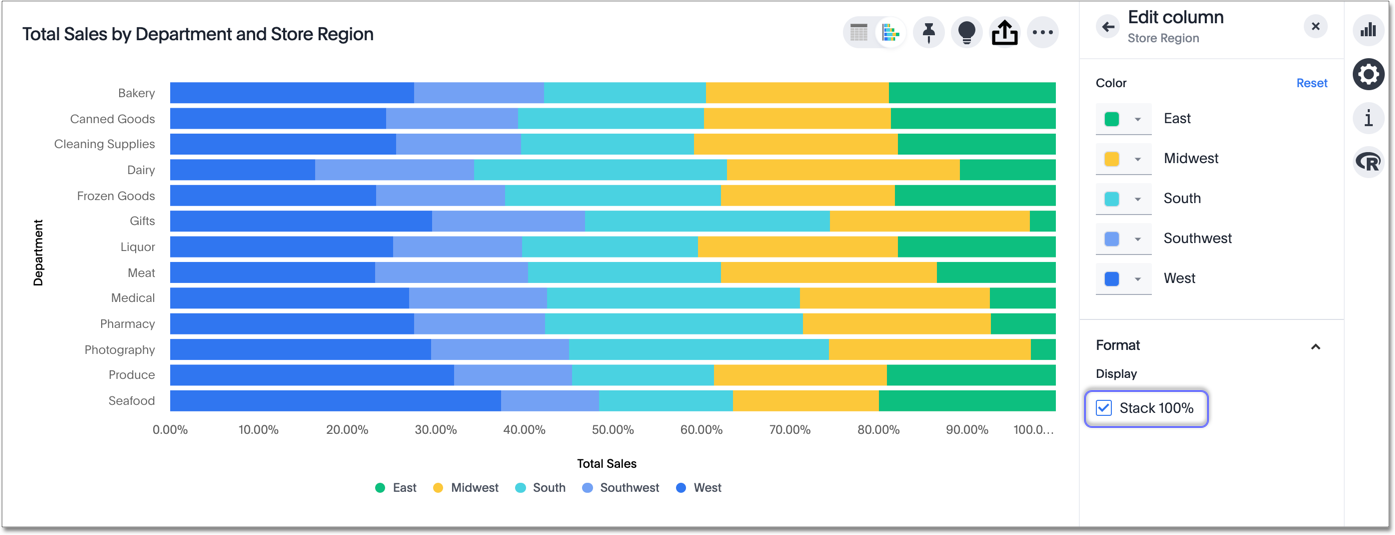
However, if you apply the wrong chart type to your data, you risk confusing your users or leading them to make bad decisions. In these cases, it is preferable to use stacked area charts or stacked densities charts; With a 100% stacked bar chart there is no overall comparison, but you can compare the outer element as there are now two common baselines.
This type of graph helps compare proportions within each category. The series with the same stack value will be in the same category. Stacked bar charts are designed to help you simultaneously compare totals and notice sharp changes at the item level that are likely to have the most influence on movements in category totals.
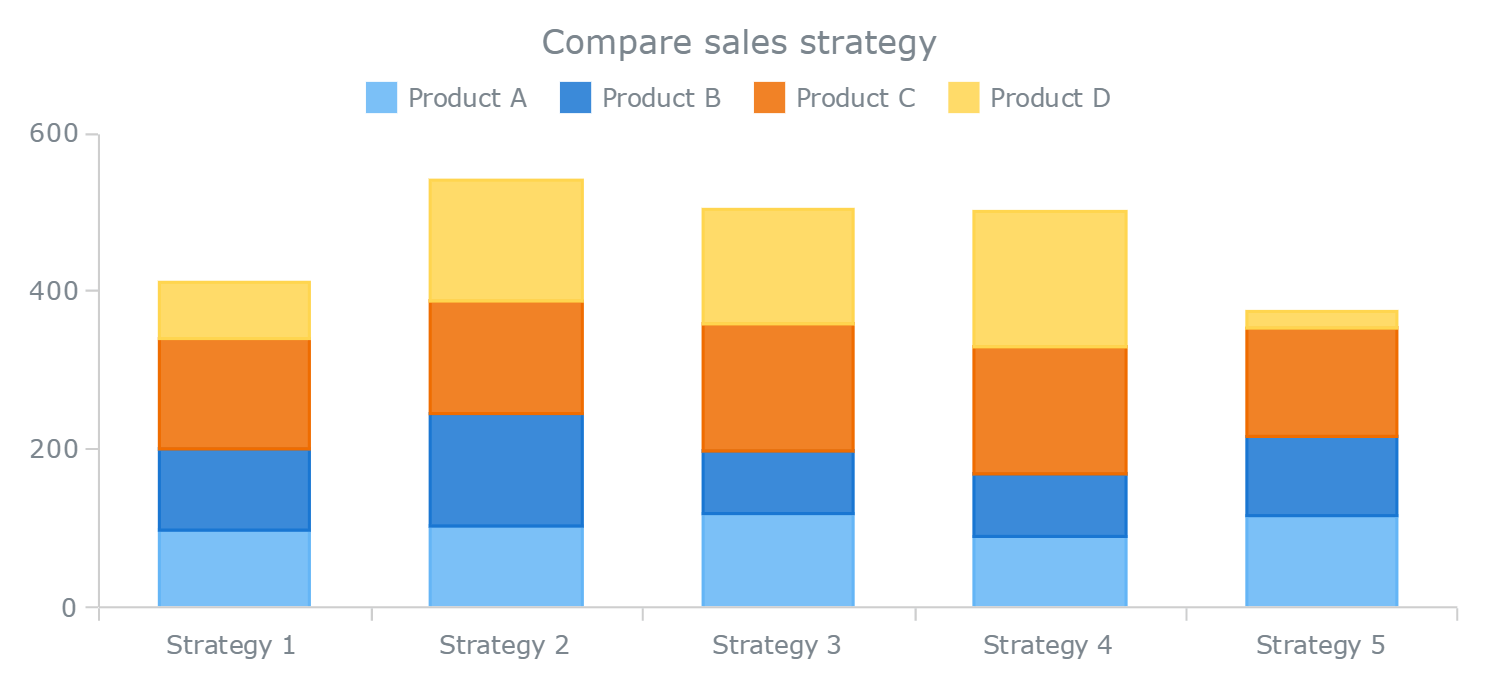
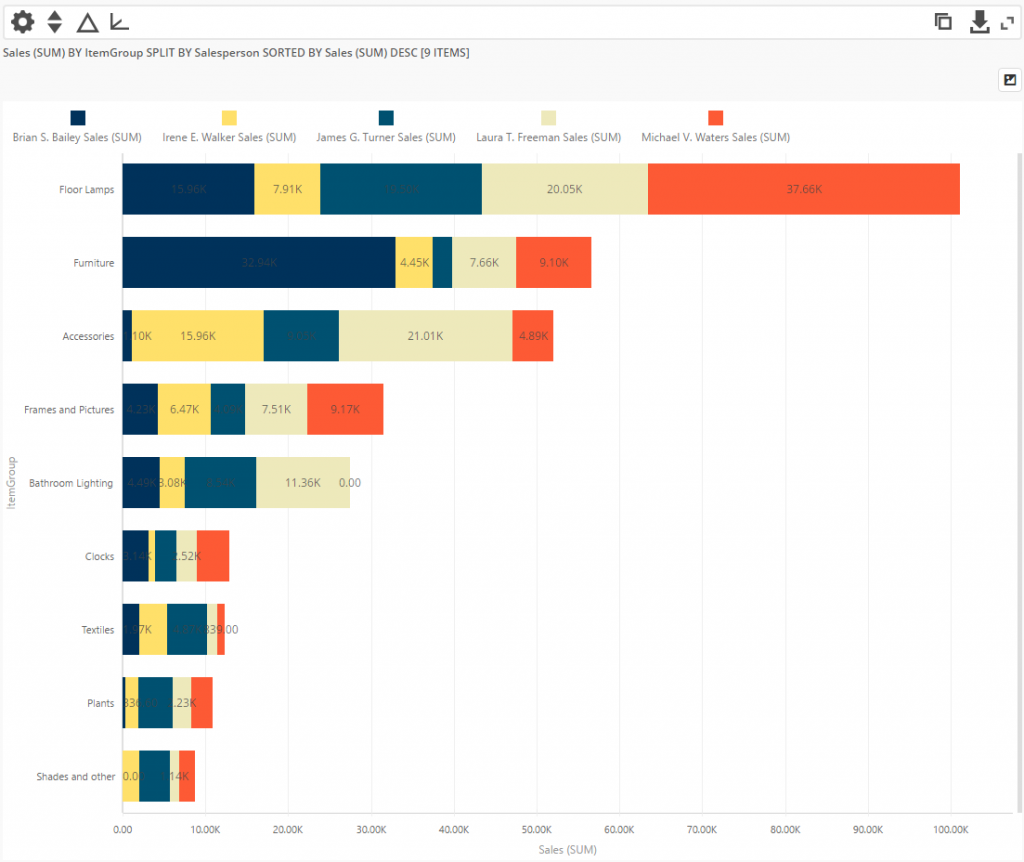
More erratic and lack a common horizon. For example, try to identify the longest bar for each colour in the chart below. Stacked bars work well when you want to compare totals across different categories, and then within a given category, you want some understanding of the subcomponent pieces.
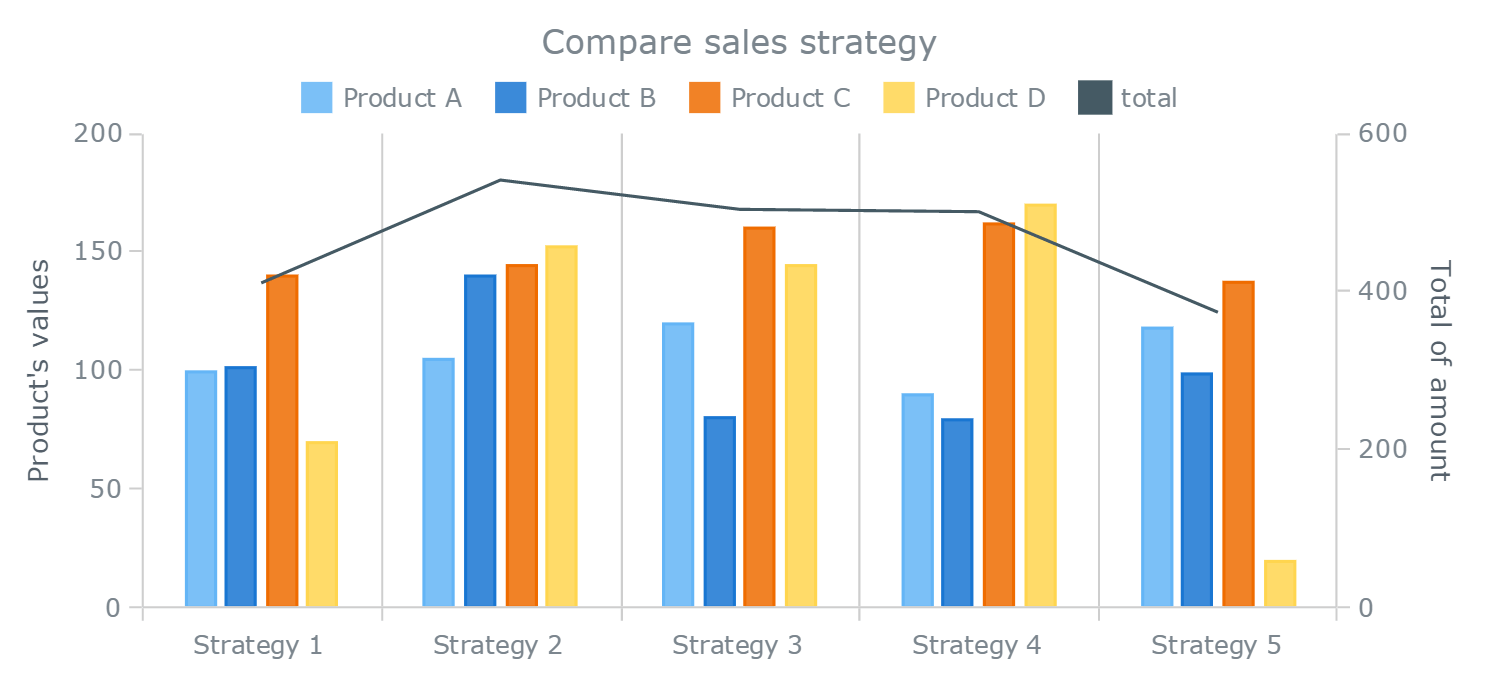
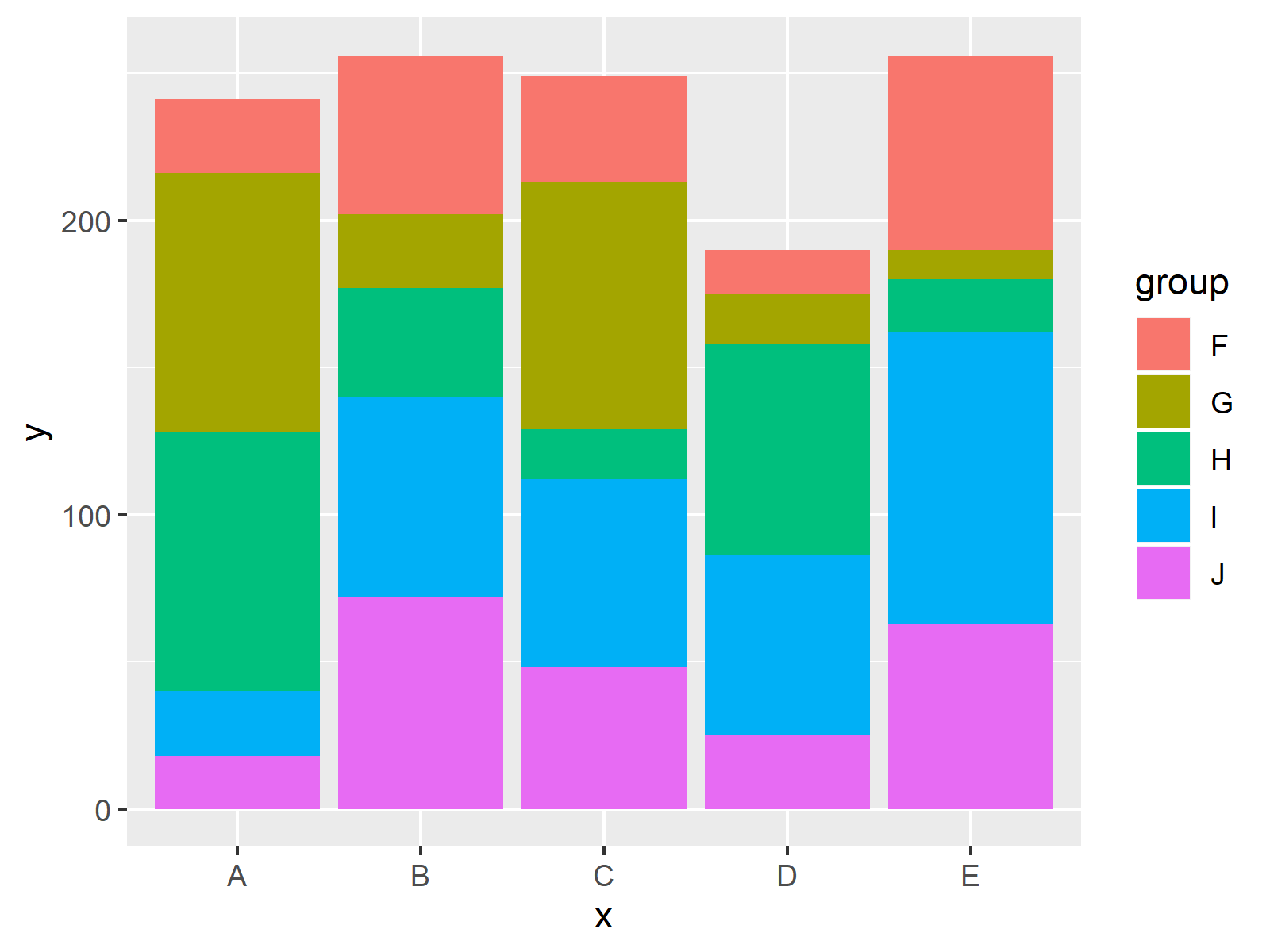
Too many bars in a bar chart make it confusing and hard to read. So, what’s not to love about stacked bar charts? A stacked bar chart is a graphical representation where multiple data series are stacked on top of one another in either vertical or horizontal bars.
That is more than ordinary when we’re working with hierarchical categories — in other words, when we have groups and subgroups that we need to visualize. Maarten lambrechts, cc by sa 4.0. You need to set the same string type value for a group of series in stack.
While a pie chart or line graph is a great tool for tracking business expenses and savings, stacked bar charts are better to compare and analyze data. A 100% stacked bar chart is a graph that shows the relative percentages of each value for each category. Standard scatter charts, line charts, and bar charts are great for visualizing a wide variety of numerical and categorical data.
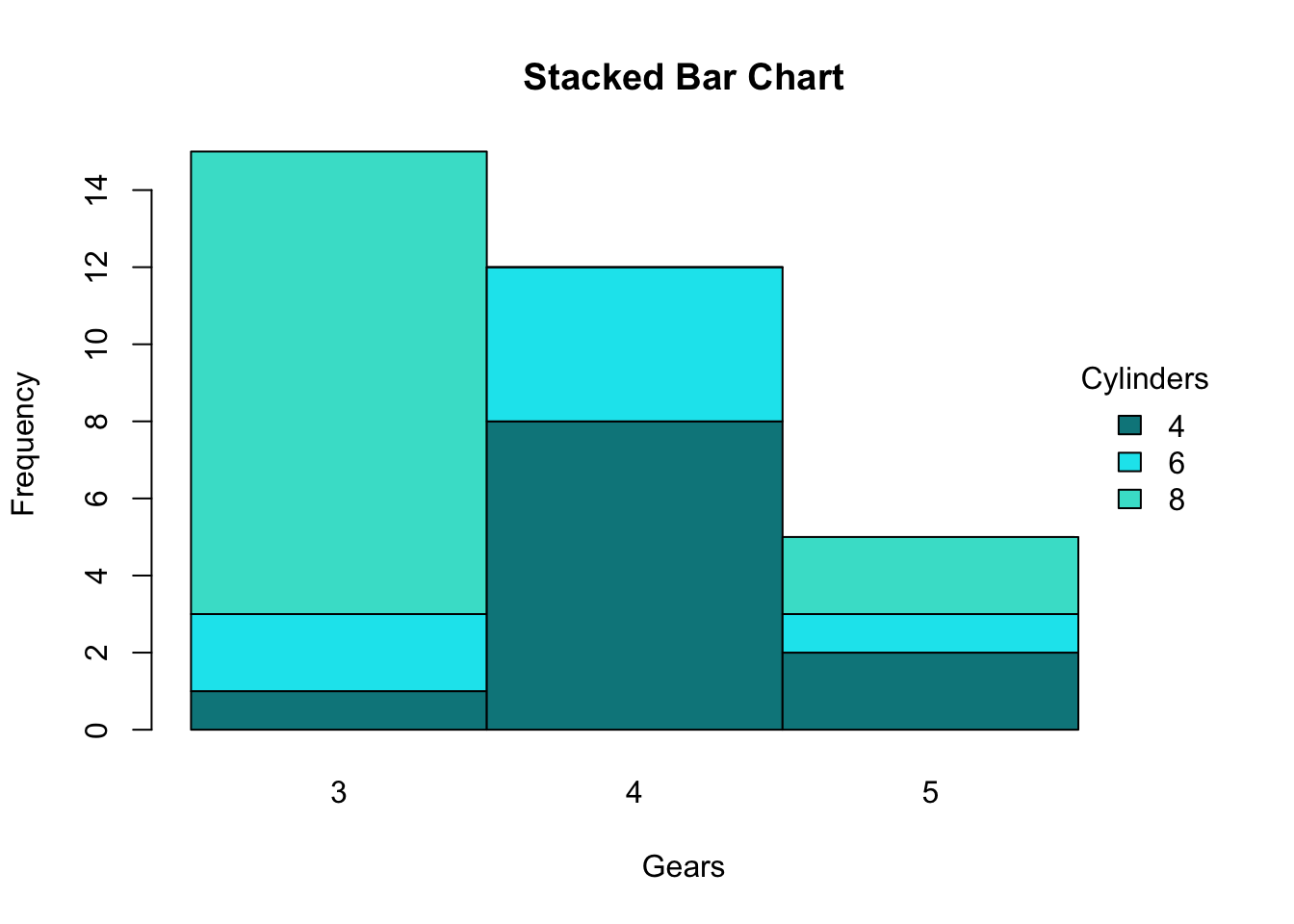
Stacked bar chart takes too much effort to understand the trends of varieties being displayed in the middle. A stacked bar chart, also known as a stacked bar graph or segmented bar graph, uses segmented vertical or horizontal bars to represent categorical data. A friendly debate with stephen few on the use of 100% stacked bar charts.
But stacked bars work less well when it is important to be able to compare the values within the stacked group of bars. Of course you know the answer as you can only compare one segment with a regular stacked bar chart and two with a 100% stacked bar chart. Additionally, they can be effective at revealing trends that.
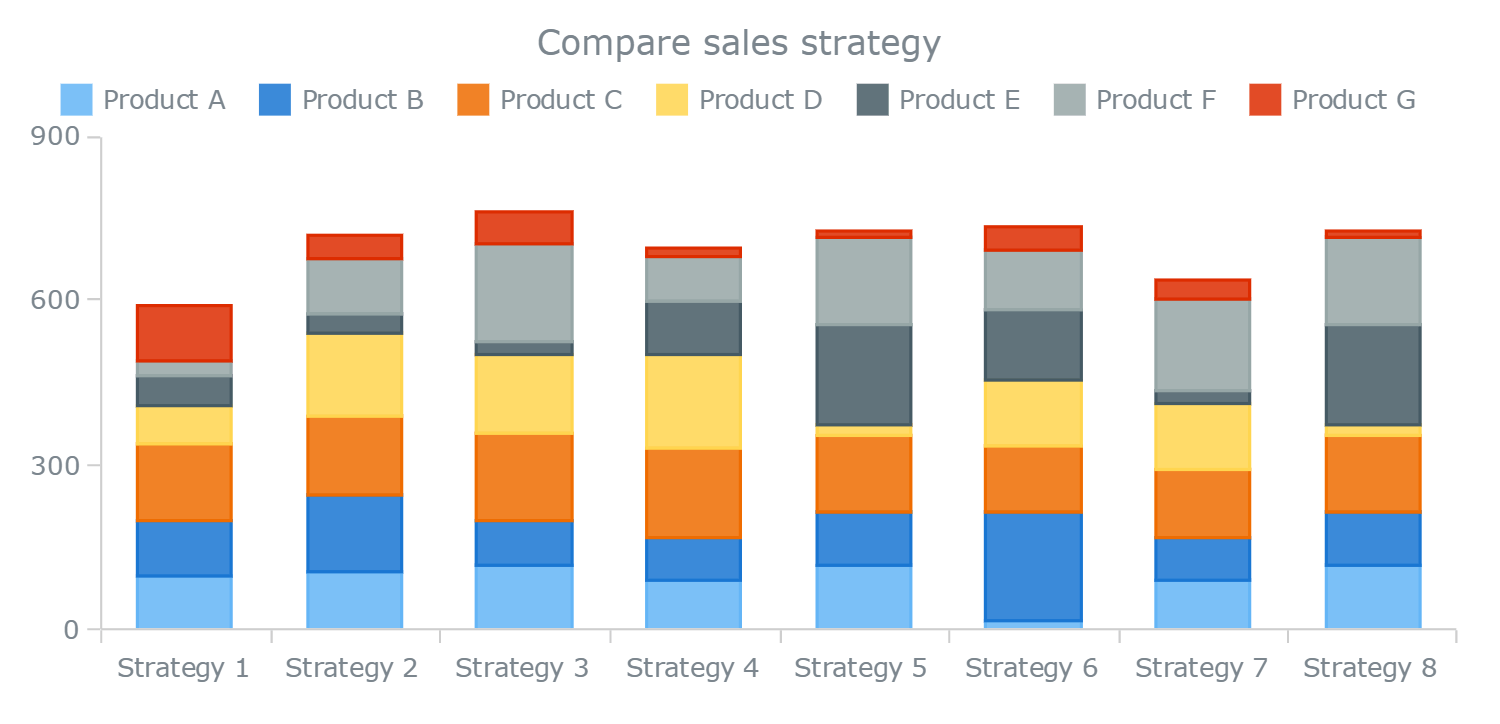
While data visualization sits at the intersection between science and art, one should make design choices that are intentional. In this guide, we’ll aim to rectify these mishaps by sharing examples, clarifying when you should (and shouldn’t) use a stacked bar chart, and discussing best practices for stacking bars. One major flaw of stacked bar graphs is that they become harder to read the more segments each bar has.






![How To Create a Stacked Bar Chart? [+ Examples] Venngage](https://venngage-wordpress.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2022/01/BarLineChart-New.gif)